Sustainability Unit
The Sustainability Unit’s update is here!
The Sustainability Unit has articulated a new vision and mission:
Vision: Establish ADG and its subsidiaries as strategic, data-driven, and industry-leading sustainable businesses with a “AAA” MSCI ESG Rating by 2030
Mission: Support ADG’s business verticals to create value by optimizing current business performance and resilience, scaling businesses, and fostering strategic partnerships
As a first step to achieving the vision and mission, ADG and its subsidiaries are undergoing a sustainability baselining exercise. We have engaged MSCI (Morgan Stanley Capital International) to provide an objective, third-party analysis of where we stand in terms of sustainability compared to industry peers. By the end of the year, ADG and its subsidiaries will receive their first ESG rating, thus providing our starting point. Once we receive our rating, we will create a targeted and tactical roadmap to achieve a “AAA” rating by 2030.

A few key points about the MSCI ESG Rating:
- A “AAA” rating means that a company is meeting global best practice regarding ESG management practices. This has a double benefit of providing management with performance feedback as well as signaling competence to investors and potential strategic partners.
- ESG Ratings are industry specific. This is because companies will face different ESG risks depending on the industry they operate in. Therefore, it allows apples-to-apples comparison against competitors that are facing the same issues.
- ADG and the business verticals will each receive their own independent ESG Rating (6 ratings total)
- The ESG Rating will be calculated based on scores across 3-6 key issues
- ADG is classified as an industry conglomerate and so the key issues we’ll be measured against are:
- Environmental Pillar: Opportunities in Clean Technology
- Social Pillar: Labor Management
- Governance Pillar: Corporate Governance and Corporate Behavior
The Sustainability Glossary
- Business Sustainability: The practice of doing business without negatively impacting the environment, community, or society as a whole across the value chain.
- ESG: Stands for environmental, social and governance issues that companies need to manage to drive their sustainability efforts. ESG metrics
- ESG Reporting standards: Refers to specific quality requirements for reporting. It contains detailed ESG metrics of “what” should be reported on a specific topic.
- ESG Ratings: Provides a simplified scale to help compare company ESG performance. Works similarly to a credit rating.
- Integrated reporting: “a new approach to corporate reporting that integrates financial information & non-financial (ESG) the act of practice of making a product, policy, activity, etc. appear to be more environmentally friendly or less environmentally damaging than it really is”
The Glossary in Practice
- As companies are integrating sustainability into their everyday business practices, they are using ESG metrics to quantify their impact. In other words, sustainability is integrated into the business approach and corporate ethos and ESG is how companies quantify it.
- There are multiple ESG reporting standards that are used globally to unify how companies are communicating their efforts. A few of the most well-known include GRI, ISSB, and SASB. There is an ongoing effort to consolidate these standards to simplify the reporting process for companies.
- Companies are beginning to publish annual sustainability reports in addition to their annual reports. The current best practice calls for integrated reporting, which combines the annual financial report and the sustainability report in one document. This signals that a company is properly embedding sustainability into its core business approach and linking it to financial value creation.
- Once companies report their ESG practices, there are specialized firms that analyze these reports and create ESG Ratings using specific methodologies. The purpose is to help investors compare ESG performance across companies. The ratings are usually on a numerical or alphabetical scale. MSCI ESG Ratings, Sustainalytics and ISS ESG are some of the most prominent raters.
The Quarterly Sustainability Q&A
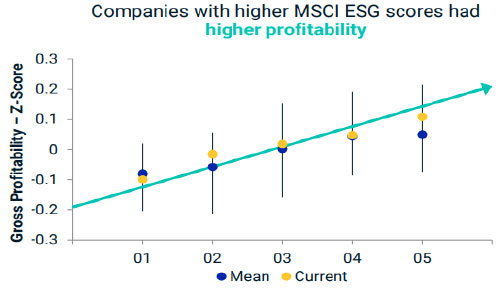
Q: Are there any financial benefits to a company being more sustainable, or is it just good PR?
A: Studies have shown a positive correlation between companies that operate sustainably and increased profitability and higher returns on investment. This is because more sustainable companies are better able to manage ESG risks. It is no longer a “nice-to-have” but rather a “must have”.
Source: Guise, G., Nagy, Z., Lee, L, Melas, D., and Nishikawa, L. 2017. “Foundations of ESG Investing, Part 1: How ESG affects Equity Valuation, Risk and Performance” MSCI Research Insight. The MSCI KLD 400 Social Index was launched